Besides helping business owners keep track of their businesses' financial health, the balance sheet offers a means to realize the coming-in crisis. Failing to review their balance sheets often makes the leader lead their business into utter chaos and indecisiveness. On the other hand, successfully creating and revising balance sheets helps you take strategic action to strengthen your company's financial standing.
Balance sheets are also important for informing banks of your company's eligibility for extra loans and credit. Current and potential investors may better understand where their money will go and what they can expect in the future, thanks to balance sheets. Let's explore how to make a balance sheet easily and accurately. We will also explore the stepwise process to make the balance sheet with examples.
| "Unlock Financial Insights with Tally Solutions: Simplify Balance Sheet Preparation for Informed Financial Management" |
What is a balance sheet?
A balance sheet is just a company's financial picture at a certain point in time. It displays what a firm possesses (assets), what it owes (liabilities), and the value retained by its owners (equity). This document gives an in-depth overview of a company's financial health and stability. Assets include anything from cash and inventory to buildings and intellectual property. Liabilities include debts and obligations. The gap between assets and liabilities is equity or net worth. A balance sheet is an effective tool for measuring a company's resources and responsibilities, which is essential for decision-making and financial analysis.
How to prepare a balance sheet?
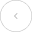
A balance sheet may appear complicated, yet it is a simple procedure that anybody can follow. Here's how you can create a balance sheet:
Prepare ledger accounts
Organized record-keeping is at the heart of balance sheet preparation. Begin by classifying financial transactions into separate ledger accounts. These accounts operate as bins for various sorts of financial transactions. You'll have accounts for assets like cash, inventory, and equipment and liabilities like loans and accounts payable. Accurate and thorough ledger entries guarantee that all financial transactions are recorded, creating the groundwork for an error-free balance sheet.
Create a trial balance
After you've updated your ledger accounts with transactions, it's time to create a trial balance. This is a list of all ledger account balances broken down into debit and credit columns. The trial balance's principal purpose is to validate that the total of debit balances equals the total of credit balances. If the two sides do not match, it indicates that your ledger entries may include inaccuracies. Before moving to the next phases, the trial balance serves as a checkpoint.
Preparing trading and profit & loss account
Before digging into the balance sheet, setting up a trading and profit and loss account is critical. This account gives information on a company's financial performance over a certain period. It shows money collected and costs incurred, resulting in a profit or loss. This step is important because it thoroughly explains how the company's operations have affected its financial position. This information provides a complete view of the company's financial health when combined with the balance sheet.
Prepare a balance sheet
You're now ready to create the balance sheet, armed with accurate trial balances and profit/loss statistics. The balance sheet is split into assets, liabilities, and equity. On the assets page, you'll include everything the company possesses, including cash, inventory, property, etc. On the opposite side, you'll outline the company's liabilities, such as loans, accounts payable, other commitments, and equity, representing the owners' residual worth. The objective of the balance sheet is to offer a picture of the company's financial status at a certain point in time—an important resource for decision-making and analysis.
Following these four procedures attentively will allow you to confidently construct an accurate balance sheet that provides a complete picture of your company's financial health, making it a useful tool for business management and planning.
Importance of balance sheet
The balance sheet functions as a financial compass, guiding both companies and investors. It provides a snapshot of a company's financial health at a certain point in time, offering a clear image of its assets, liabilities, and equity. This document assists in determining the solvency, liquidity, and general stability of a company. It helps companies make strategic decisions such as securing loans, planning investments, and analyzing growth potential. Investors use the balance sheet to assess a company's worth and possible risks. The balance sheet is a strong instrument for making educated financial decisions affecting short-term operations and long-term success.
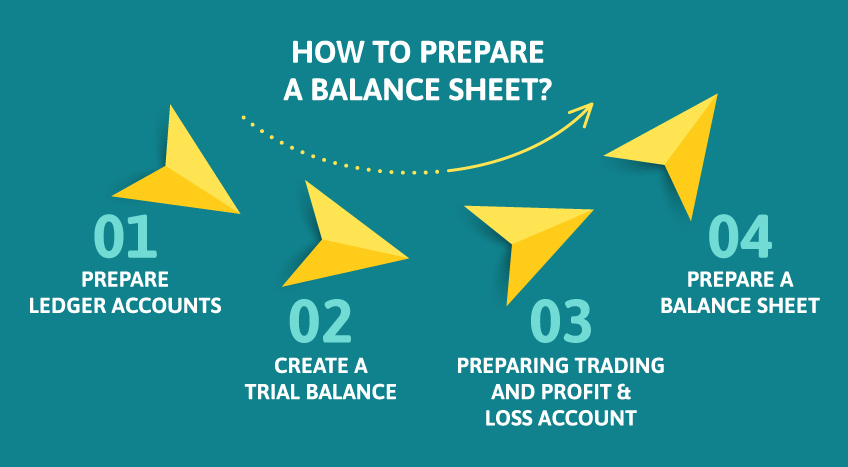
What is the formula for a balance sheet?
A company's assets, liabilities, and equity are balanced to create a balance sheet. Total assets are equal to total liabilities plus total equity. The aggregate of all short-term, long-term, and other assets is referred to as total assets.
Balance sheet prepared by modern day business
The technique of balance sheet preparation has developed in modern-day business. Traditionally an annual affair, the balance sheet is increasingly critical in real-time decision-making. As a result, it is progressively being created more frequently—quarterly, monthly, or even more often. However, this is not a simple operation; compiling detailed financial data requires substantial effort and focus. To overcome this issue, many organizations have turned to accounting software, which has streamlined the process by automating the creation of balance sheets and other critical financial data. This trend points out the increased importance of balance sheets as dynamic tools that provide timely insights essential for managing today's fast-paced corporate climate.
3 Balance sheet components
The balance sheet is divided into three components that reveal a company's financial picture:
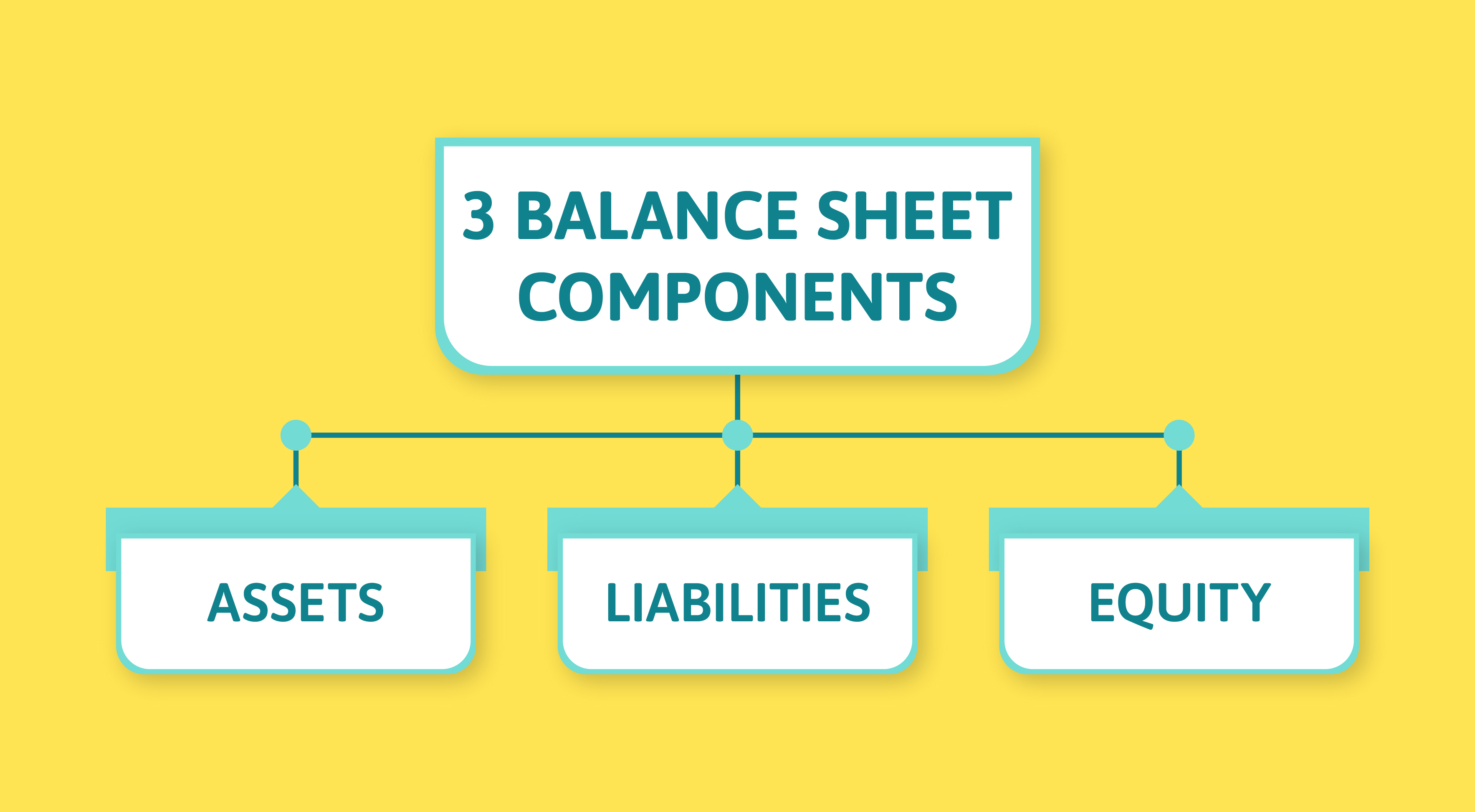
Assets
Assets include a company's cash, goods, property, investments, and other resources. These holdings demonstrate a company's ability to earn money and meet obligations. Assets are categorized as current (short-term) or non-current (long-term), which helps in determining liquidity and stability.
Liabilities
Liabilities include the company's commitments, such as debts, loans, and payables. They highlight the financial commitments that must be satisfied. Similar to assets, liabilities are segmented into current and non-current subtotals, which indicate the timing of repayment. Liabilities analysis reveals the magnitude of a company's external responsibilities.
Equity
The term equity refers to the residual interest, which represents the net worth of the company's owners or shareholders. It is computed by deducting liabilities from assets. Equity measures a company's net worth and reflects its operational success. Increased equity demonstrates growth and financial health.
Final takeaways
Building an accurate and up-to-date balance sheet is crucial for evaluating your organization's financial health. Tally Solutions, an accounting software pioneer, recognizes the changing landscape. Tally's straightforward tools enable firms to create these critical financial snapshots more regularly, providing immediate insights into their financial health. Tally Solutions simplifies the time-consuming process of gathering extensive accounting data into a simplified experience. Contact Tally Solutions today and set off on a path to more effective, precise, and informed financial management.